does autoclaving kill rnase|how to beat rnase : factories Unfortunately, RNAses are rather stable proteins and autoclaving doesn't completely kill their activity. The common methods to inactivate are unspecific methods that will destroy any enzymes, either through covalent modification or degradation. The most common methods for RNAse inactivation are: Treatment with DEPC.
Período de Controle: Autoclave nº: a Estabelecimento: Monitorização da Esterilização Registros
{plog:ftitle_list}
$2,390.00
Autoclaving is not effective at eliminating RNase in solution because the RNases simply renature as the solution cools. "Autoclaving inactivates enough of the RNase A to protect the probe from degradation up to a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Note that only a portion of the RNase is . RNase, an enzyme that breaks down RNA, and DNase, which breaks down DNA, are contaminants that can interfere with nucleotide research. DNase can be destroyed by . DNAse enzymes are pretty labile, they can even be denatured by physical force such as vortexing. RNases are much more robust. As Britta says, autoclaving alone is not sufficient, you need to eg .solutions such as Tris and does not require a 2-hour treatment or autoclaving. DEPC treatment is the most commonly used method for eliminating RNase contamination from water, buffers, and . Merely autoclaving will not destroy all RNase activity, since these enzymes are very robust and can regain partial activity upon cooling to room .
Protector RNase Inhibitor is one of the best characterized RNase inhibitors, effective on a wide spectrum of RNases (RNase A, RNase B, RNase T2) and offering the best protection of precious RNA samples. Protector RNase Inhibitor is fully active over a broad temperature range of +25 to +55°C. Even at +60°C some RNase inhibition is still measured.
Unfortunately, RNAses are rather stable proteins and autoclaving doesn't completely kill their activity. The common methods to inactivate are unspecific methods that will destroy any enzymes, either through covalent modification or degradation. The most common methods for RNAse inactivation are: Treatment with DEPC. All it could take is to leave a pipette on a desk to pick up RNase from shed skin cells or begin to use an autoclaved piece of equipment only for it to immediately begin to infer new RNase molecules from the air. Autoclaving also does not destroy all RNase activity on its own, as they can retain partial activity on cooling to room temperature. Autoclaving DOES work, to an extent The much fabled indestructibility of RNases in the face of autoclaving is true at the core, but also very over-hyped, as I mentioned above. A nice little study from Ambion showed that RNases (or RNase A at least) are not completely resistant to autoclaving. Rather their activity is decimated by autoclaving .
of the RNase is inactivated by autoclaving, otherwise the RNA probe would remain intact at any RNase concentration. Autoclaving alone may be sufficient to eliminate enough RNase for some applications.
We buy RNase/DNase-free tubes and still autoclave them. They get poured from the big bag into containers and autoclaved. Filter tips are also RNase/DNase free but don't get autoclaved. We use Qiagen kits to extract RNA. The only tubes and water used in this protocol come with the kit so you don't have to worry about making sure your own tubes .Merely autoclaving will not destroy all RNase activity, since these enzymes are very robust and can regain partial activity upon cooling to room temperature. Always use tips and tubes that have been tested and certified RNase-free. Ambion has a .Use RNase-free solutions, and RNase-free certified, disposable plasticware and filter tips. Maintain a separate area for RNA work and carefully clean the surfaces. Decontaminate glassware by baking at 180 degrees Celsius or higher for several hours or by soaking in freshly prepared 0.1 percent (v/v) DEPC in water or ethanol for 1 hour, followed .Use RNase-free solutions, and RNase-free certified, disposable plasticware and filter tips. Maintain a separate area for RNA work and carefully clean the surfaces. Decontaminate glassware by baking at 180 degrees Celsius or higher for several hours or by soaking in freshly prepared 0.1 percent (v/v) DEPC in water or ethanol for 1 hour, followed .
"Autoclaving inactivates enough of the RNase A to protect the probe from degradation up to a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Note that only a portion of the RNase is inactivated by autoclaving, otherwise the RNA probe would remain intact at any RNase concentration. Autoclaving alone may be sufficient to eliminate enough RNase for some applications."As you rightly say, autoclave water is not RNAse free, nevertheless RNAses will resist your autoclaving process if present in your plastic. Doing this you'll eventually disrupt DNases and other .Controlling RNase Contamination Working with RNA can be intimidating. Environmental RNase contamination sources include microbial contamination from room air as well as RNases from human skin, hair, or saliva. RNase inactivation methods range from DEPC treatment followed by autoclaving to more Does autoclaving destroy RNase and DNase? RNase, an enzyme that breaks down RNA, and DNase, which breaks down DNA, are contaminants that can interfere with nucleotide research. DNase can be destroyed by autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121°C (250°F) or by following any of the procedures listed below. .
Autoclave to kill RNases/DNases? - argument (Dec/14/2004 ) . If it dose kill RNase, why we need to treat water with DEPC and then autoclave it? Autoclaving is not effective at eliminating RNase in solution because the RNases simply renature as the solution cools.
rnase super powers
rnase inhibitor removal
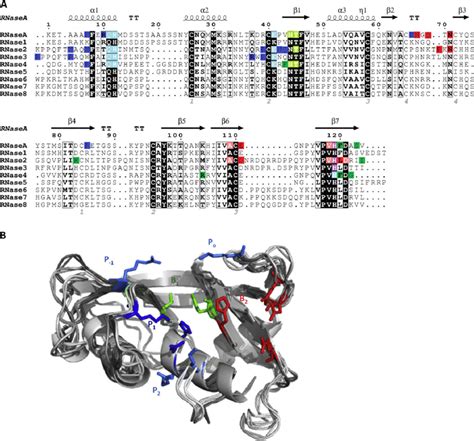
Because ribose residues carry hydroxyl groups in both the 2' and 3' positions, RNA is chemically much more reactive than DNA and is easy prey to cleavage by contaminating RNases-enzymes with various specificities that share the property of hydrolyzing diester bonds linking phosphate and ribose resid .
Autoclaving alone does indeed inactivate a substantial amount of RNase A (Figure 1). Various concentrations of RNase A were added to PBS and autoclaved. Aliquots of each solution were mixed with a 304 base 32P-labeled RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour, followed by electrophoresis and exposure to film. . Effect of Autoclaving on .
Especially RNase A (structure on top) is scary for RNAs and RNA researchers. Some guidelines on how to best avoid RNase contamination. Contents. . Whenever possible treat solutions with 0.1% DEPC for 1 hour at 37°C and autoclave 15 mins at 15 psi. Remove RNases from glassware by Bake glassware at 300°C for 4 hours or 180°C or higher for .
RNase, an enzyme that breaks down RNA, and DNase, which breaks down DNA, are contaminants that can interfere with nucleotide research. DNase can be destroyed by autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121°C or by following any of the procedures listed below. One or more of the following techniques will inhibit or remove RNase from your plastic container.
What does RNase do? RNases catalyze cleavage on RNA, which contributes to the degradation of RNA. They break the bonds between nucleotides, breaking RNA into smaller components and allowing access to other enzymes. RNases are usually considered contaminants in labs where researchers work with RNA because it lessens RNA integrity and sample quality.These RNases are resistant to metal chelating agents and some of them, like RNase A family enzymes, can survive prolonged boiling or autoclaving. RNase A-type enzymes rely on active site histidine residues for catalytic activity (1) and can be inactivated by the histidine-specific alkylating agent diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC).Autoclave to kill RNases/DNases? - argument (Dec/14/2004 ) . If it dose kill RNase, why we need to treat water with DEPC and then autoclave it? Autoclaving is not effective at eliminating RNase in solution because the RNases simply renature as the solution cools.Autoclave tips, tubes, and solutions to help inactivate RNases. Glassware can be baked at 300°C for four hours and plasticware, tubes, and most solutions can be DEPC-treated. . To identify if RNase contamination has occurred in your lab, RNase detection kits are available. These kits help allow researchers to identify contaminated reagents .
more convenient) before use. Autoclaving alone will not fully inactivate many RNases. Alternatively, glassware can be treated with DEPC* (diethyl pyrocarbonate). Fill glassware with 0.1% DEPC (0.1% in water), incubate overnight (12 hours) at 37°C, and then autoclave or heat to 100°C for 15 minutes to eliminate resid-ual DEPC.What does RNase do? RNases catalyze cleavage on RNA, which contributes to the degradation of RNA. They break the bonds between nucleotides, breaking RNA into smaller components and allowing access to other enzymes. RNases are usually considered contaminants in labs where researchers work with RNA because it lessens RNA integrity and sample quality.
Autoclaving will destroy the untreated DEPC which could react with RNA. . So, does RNAseZap actually destroy RNAse activity, or is it simply a "good detergent" to pick them up and rinse them away?
how to fight rnase
how to defeat rnases
– Utilizada para o fechamento de pacotes que serão esterilizados em autoclave. – Funciona como indicadora de esterilização, pois possui listras diagonais de tinta termo reativa que mudam sua coloração de branco para preto, quando .
does autoclaving kill rnase|how to beat rnase